The product development cycle, also known as the product development lifecycle, is the process of creating and introducing new or improved offerings to the market.
It involves identifying opportunities for new products or features, or improvements to existing products or features, which should align with customers’ pain points and unmet needs. Other product development lifecycle stages include: conducting research, validating concepts, gathering customer feedback and developing and launching the product.
A successful product launch requires careful planning, execution and iteration. In my career as a product manager, I have worked on both large and small product development, and both come with their own sets of challenges. I have learned, however, that with the right strategies and techniques, you can improve your chances of success.
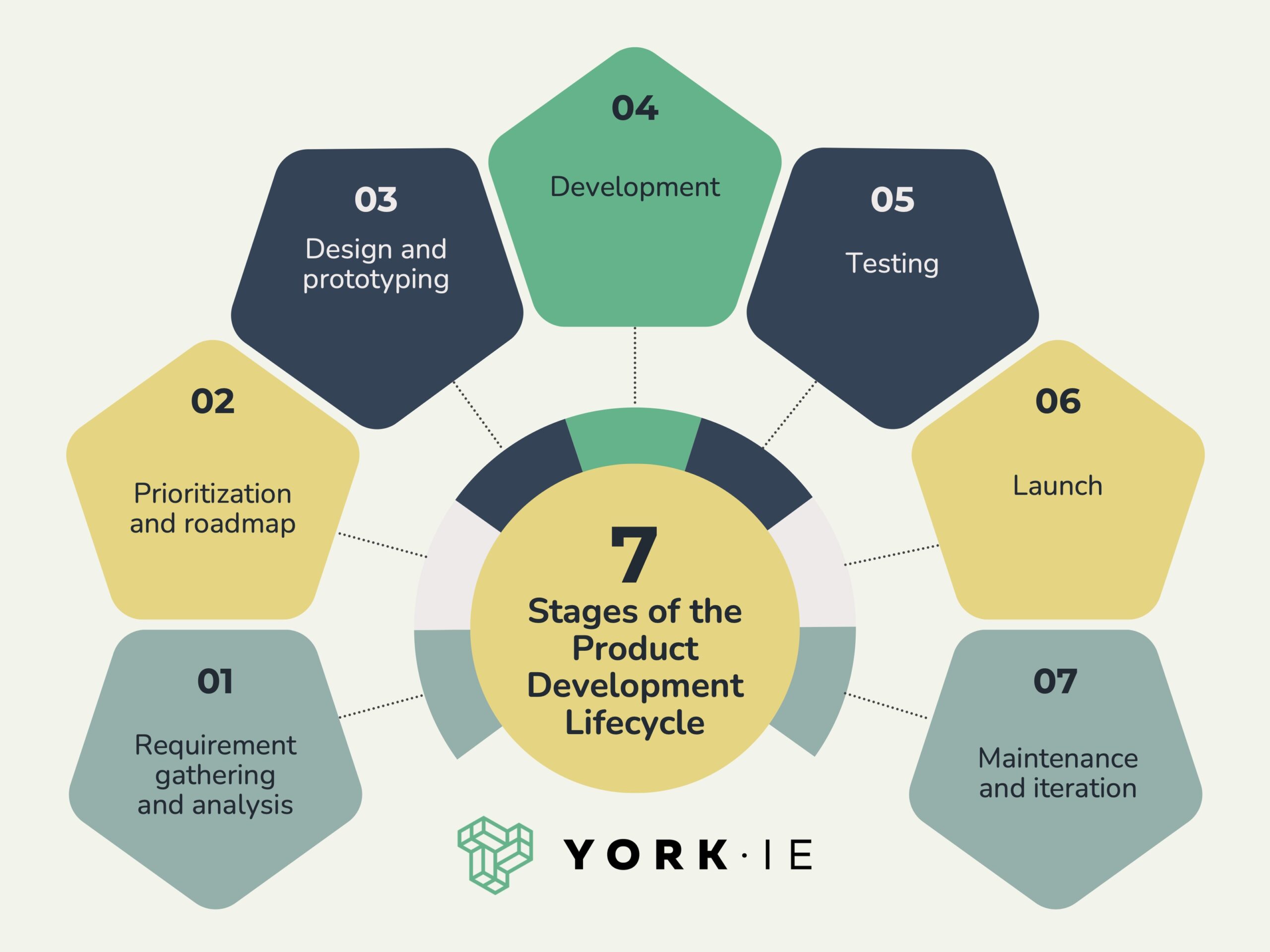
The 7 Product Development Lifecycle Stages
The seven stages of the product development cycle are:
- Requirement gathering and analysis
- Prioritization and roadmap
- Design and prototyping
- Development
- Testing
- Launch
- Maintenance and iteration
1. Requirement Gathering and Analysis
In the first stage of the product development cycle, the requirements are reviewed and analyzed to determine product vision, define product goals and identify the functions and features that the product must provide.
2. Prioritization and Roadmap
Once we understand the product goal and vision and list all the features, the next step is to prioritize the features into must-have, should-have and nice-to-have categories and create a product backlog. Based on those priorities, define your minimum viable product (MVP) and build a product roadmap with timelines and milestones.
3. Design and Prototyping
The goal at this stage is to get a clear understanding of how the product is going to look and function. Creating a prototype with the same look and feel can help stakeholders better envision the final product.
4. Development
This is the phase where the product is actually created and brought to life. It involves building and testing the product to ensure it meets quality standards. To stay on top of product performance, keep building and releasing small, iterative updates to the product over time.
5. Testing
In this stage of the product development cycle, the product is end to end tested to ensure that it meets the requirements and functions correctly. This includes testing for functions, usability, and security.
6. Launch
Your MVP is something between a prototype and a finished product, which allows you to deliver something of value to your customers. It is a version of your product that allows you to gather feedback and continue tweaking.
7. Maintenance and Iteration
In this last stage, the goal is to maintain and improve product performance by identifying and resolving defects — and, in parallel, start planning for additional features and functionalities that were not included in the MVP.
Product Development Cycle Milestones
Milestones are similar to product development lifecycle stages, but they specifically represent achievements reached on your journey towards building a successful product.
This is a simple but effective way to think about your product development cycle milestones:
- Idea generation
- Concept design
- Implementation
- Product launch
- Product growth
1. Idea Generation
The first milestone in product development is identifying a need and coming up with an idea to meet that need. The best way to do this is to understand your potential customers’ pain points and unmet needs.
An example of a product built out of need is Uber. There were very specific needs that were not being met by traditional taxis or car services, and it caused a lot of problems for people who relied on those forms of transportation. Uber disrupted those industries and met those needs with an on-demand ride-hailing app.
2. Concept Design
You reach the next milestone when you refine your idea into a clear and concise product concept. This process can involve creating a detailed product specification and identifying potential risks, costs and benefits. To design your concept, follow these steps:
- Create a problem statement.
- Define high-level acceptance criteria.
- Determine if it’s a new product, new feature or improvement in current functionality.
- Create a product roadmap.
3. Implementation
The next milestone in the product development lifecycle comes when the product is actually developed and brought to life. After the key questions are answered and design prototyping is done, it is time to start implementing the designs, architecture and structure that you defined as your acceptance criteria. It is also important to continue testing the build to ensure the product meets quality standards.
4. Product Launch
To fully bring your idea to life, launch it to market by implementing the go-to-market (GTM) strategies you have developed alongside the product.
5. Product Growth
As you gain traction in the market, you’ll continue to refine and iterate on your product based on customer feedback. Once you have found product market fit and established a repeatable GTM motion, consider expanding the product line or exploring new markets.
For an example of a company’s successful actions in the product growth stage, look at Meta’s Instagram. Instagram originally found success as a platform for users to share images and videos, then expanded to vertical videos called Reels. Instagram changed its algorithm to surface more Reels in users’ feeds, and many content creators, influencers and brands found that they earned more views and higher engagement rates by posting Reels. As a result, Instagram further grew its user base.
4 Types of Product Development
The four types of product development are:
- New product development
- New feature development
- Enhancement to existing feature
- Rebranding
All of these types should roughly follow the same product development lifecycle stages and have the same milestones.
1. New Product Development
New product development involves creating a product from scratch and bringing it to market. As discussed above, Uber is an example of a new product that was developed to solve customer problems with existing solutions.
2. New Feature Development
New feature development is the addition of major new functionality to an existing product. You can’t just build your product and then be done; it’s important to plan for expanded functionality so you can stay on top of users’ preferences. As mentioned earlier, Instagram Reels is a perfect example of this product development type.
3. Enhancement to Existing Feature
This involves making improvements to existing functionality. These may happen behind the scenes, such as with performance and security upgrades, or they may be more apparent to users, like the option to make your profile private on Facebook.
4. Rebranding
Rebranding means so much more than just a new font or icon. It involves completely repurposing your product or feature to target new markets or meet new customer needs.
Keys to a Successful Product Development Cycle
The foundation of a successful product is based upon a strong relationship between the business and the product team. A deep understanding of customer needs, a clear value proposition, quality development, effective marketing, customer support and continuous improvement must all be part of your product development lifecycle.
The journey from idea to product can be time-consuming and challenging, but with strategic planning, organization, persistence, hard work and a willingness to learn and adapt, you can turn your idea into a successful product.